The five types of underground coal mining are drift mining, shaft mining, pillar mining, continuous mining, and longwall mining.
1. DRIFT
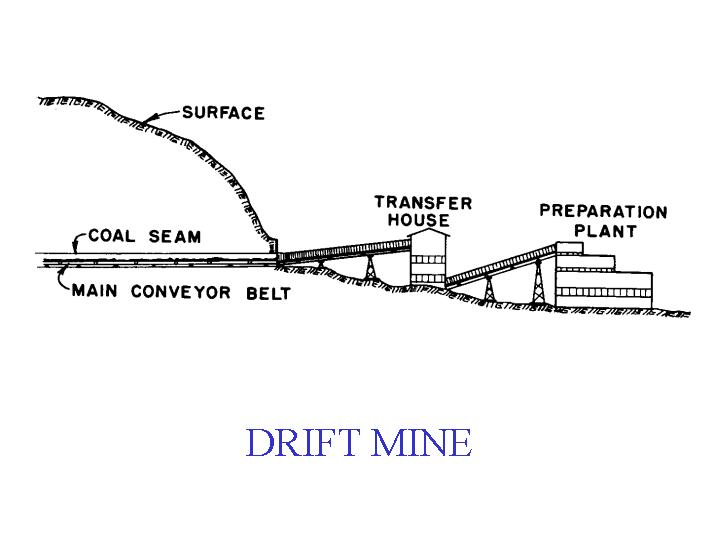
Drift mining is where the coal seam intersects with the surface. The mine enters the seam in a horizontal direction, following the coal. Drift mining was one of the earliest mining techniques.
2. SHAFT
Shaft mining is a common method of accessing coal seam, where elevators take you down to the
mines. Shaft coal mines in West Virginia are deeper than 1000 feet below the surface. It's a very
simple system because the coal can be transported right to the surface and shipped off.

3. ROOM AND PILLAR
Room and pillar mining isn't the greatest type of mining, because nearly half of the coal has to be left
behind to support the mine roof. Pillars can "squeeze" which puts pressure on the adjacent pillars,
leading to roof collapse. Pillar mining is the mining method that has the most roof collapses, therefore it is a constant danger.
4. CONTINUOUS
Continuous mining machines can be used with drift or room and pillar mines. One miner can operate a
continuous mine machine to a rotating steel drum with tungsten carbide teeth to mine 5 tons of coal per
minute. Different kinds of continuous mining machines, have been used since 1940. Continuous mining
uses more machines than people. The machines have conveyor systems that transport the coal out of the mine as soon as it's mined.

5. LONGWALL
Longwall mining is a highly efficient method of mining. Huge mining machines hold the roof up with
hydraulics, as it removes coal. Once the machine gathers enough coal, it retreats, allowing the roof to collapse behind it. Longwall mines collect a lot more coal than room and pillar mines do.







